This lesson will cover the most basic principles of cryptocurrency in a nutshell. More experienced students and traders, already familiar with these topics, can also skip this section. This introductory lesson is for new traders who are not yet familiar with the concepts cryptocurrency and blockchain, or for anyone who is interested in these topics. If you have read this, you will know more about crypto than the average person.

Cryptocurrency has become a global phenomenon, which few people have missed. Still many people do not understand exactly what it means. Many banks, governments and companies are now aware of the potential importance of crypto. Meanwhile, most major banks, software companies and governments have already paid attention to it by investigating or starting a project themselves.
But the vast majority of the population, including many bankers, scientists and developers, have in fact limited knowledge about crypto. Often one does not even know the basic concepts. Therefore, I have written this introduction to answer the most basic questions.
- What is cryptocurrency?
- Where does cryptocurrency come from?
- What do you need to know about cryptocurrencies?
What is cryptocurrency?
What is cryptocurrency (crypto), is it a hype? Like the dotcom bubble. Or is it the money of the future? Cryptocurrency actually arose as a by-product of another invention. Satoshi Nakamoto, the unknown inventor of Bitcoin – the first and still most important crypto, never intended to invent a new payment method. In his announcement of Bitcoin at the end of 2008, Satoshi said that he had developed a “peer-to-peer electronic cash system”:

“Announcing the first release of Bitcoin, a new electronic cash system
that uses a peer-to-peer network to prevent double-spending.
It’s completely decentralized with no server or central authority.”
– Satoshi Nakamoto
After all centralized attempts failed, Satoshi tried to build a digital money system without a central entity. Just like a peer-to-peer network is used for file sharing. That was the beginning of cryptocurrency. This was the missing piece that enabled Satoshi to make digital money. The reason is somewhat technical, but if you understand it, you know more about cryptocurrencies than most people.
“… after more than a decade of failed Trusted Third Party
based systems (Digicash, etc), they see it as a lost cause.
I hope they can make the distinction,
that this is the first time I know of
that we’re trying a non-trust based system.”
– Satoshi Nakamoto
Cryptocurrency is a kind of digital currency, which is often used as an alternative money system for the regular types of money. The world’s most famous cryptocurrency is the bitcoin. The extent to which cryptocurrency really is money is controversial. The market capitalization of cryptocurrency is estimated at 100 to 200 billion dollars in 2018.
Cryptocurrency is registered in a blockchain (click for more info on what a blockchain is). Sometimes there is a separate blockchain for a single cryptocurrency, in other cases one blockchain registers multiple currencies and / or other data. The data per transaction is the public key of the new owner, a hash of the combination of the data of the previous transaction and this public key, and the digital signature of the previous owner. The new owner often can not easily check if one of the previous owners has not spent the amount several times. This is done by a network of nodes that each have an overview of all (recent) transactions.
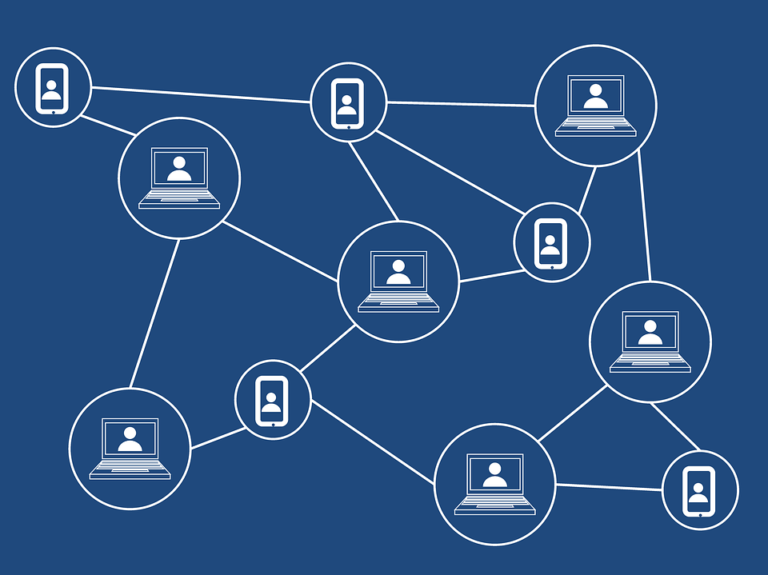
(Above: Simplified decentralized network structure)
It can therefore take a while before the new owner has sufficient certainty about this. That takes at least until the transaction is processed in a block. Depending on the cryptocurrency, this can take a long time if the payer pays a low fee in proportion to the number of bytes (regardless of the amount of the payment itself). Subsequently, as new blocks are build upon the transaction’s block, the transaction’s reversal by the network is becoming increasingly unlikely.
Often a proof-of-work scheme is used as a system of consensus based upon computing power that must provide protection against manipulation and falsification. Multiple transactions are often processed in each block (at bitcoin, for example, per block all transactions in a time interval of about 10 minutes, that is about 3000 in December 2017. As soon as a block is found, it is made public. The other nodes check it, and use this and the new transactions that have now been carried out to start with the search for a new block (hence a chain of blocks – blockchain).
Often with each new block an amount of the cryptocurrency is put into circulation by automatically assigning this to the finder of the block as a reward. This is called the mining of new monetary value. The search for a valid block is called mining. The value of cryptocurrency is determined by supply and demand, which also includes the costs of finding a new block that requires a lot of computing power and electricity for proof-of-work.

(Above: First generation mining rig)
The amount of the reward is fixed in the software (sometimes according to a predetermined schedule, this is always reduced after a number of blocks, and ultimately zero). The level of difficulty of the proof of work can also be arranged so that the block frequency remains around the desired level. This is comparable to the extraction of precious metals, whose scarcity and difficulty it takes to mine determine its value. Furthermore, the value is determined by the total amount already ‘mined’ and by the users who trade with it.
Cryptocurrency is generally based on peer-to-peer connections and is decentralized (without a central server). All variants of cryptocurrency are based on the first concept: the bitcoin. Cryptocurrency is typically designed to function as a non-inflation payment system, because only a limited amount is put into circulation. However, there are a few types of cryptocurrency, which do have a small amount of inflation.
Cryptocurrency is also designed to ensure that funds can never be frozen by authorities. Existing cryptocurrency systems are all pseudo-anonymous. It is possible to make money flows easily traceable. Transferring money is not done by name but is done on the basis of cryptocurrency addresses. Someone can generate a new cryptocurrency address for each amount received. Suggestions have been made – for example in Zerocoin – to achieve complete anonymity.
Where does cryptocurrency come from?
Early attempts to combine encryption (cryptography) with electronic currencies stem from David Chaum, who devised DigiCash and ecash to send electronic money transactions encrypted.


The first true crypto coin was Bitcoin, which was designed in 2009 by a software maker with a pseudonym of Satoshi Nakamoto. But nobody knows who he (or she) really is. This man with the same name was falsely accused of being the inventor of Bitcoin:
Bitcoin uses the hash method SHA-256 as the proof-of-work scheme.
Later, in other cryptocurrency types, decentralization was strived to make censorship on the coin more difficult, and anonymity increased. Many comparable cryptocurrency types then arose rapidly. However, they were not all successful because many had little innovation, and the markets were already full of existing types of cryptocurrencies.
During the first few years of cryptocurrency, it gradually gained more attention in the media and the public, but attention grew rapidly from 2011, especially when the price of the bitcoin rapidly increased in value in 2013 and 2017/2018.
The term altcoin has various similar definitions. Most people refer to all cryptocurrencies other than bitcoin as altcoins.
What do you need to know about cryptocurrencies?
Wallets
A wallet is used when storing cryptocurrencies. Choosing a wallet is a very important task, since it must be safe and not allow hackers to get to the coins. When using a web wallet, the private keys are managed by a trusted third party. Some web-based wallet providers use two factors (such as Google Authenticator) for extra security. In that case, a keylogger is not enough for a hacker to steal log-in data and gain access to the wallet. Cryptocurrency exchanges link the user’s wallet to their centrally managed portfolio. For example: when trading bitcoins between users on the Binance exchange, the transactions are written in their private ledger (off-chain transaction). Only when a user wants to enter his cryptocurrency in the exchange or when he wants to remove his cryptocurrency from the exchange, the transaction is written on the public bitcoin blockchain (on-chain transaction). To initiate or verify a transaction, the cryptocurrency portfolio connects to a client or node on the network to process the request.

A safer way to store the coins is to use a hardware wallet. This can be stored at home, and there is no third party involved. With this wallet a private key is generated that only the user can access. This must be kept well: if the hardware wallet is lost, the coins will disappear forever. Above an image of the popular Ledger Nano S hardware wallet.
Anonymity
Bitcoin is pseudonymous rather than anonymous in that the cryptocurrency within a wallet is not tied to people, but rather to addresses, called “keys”. Thereby, Bitcoin owners are not identifiable, but all transactions are publicly available in the blockchain. Still cryptocurrency exchanges are often required to collect the personal information of their users. With many cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, of every address all the incoming and outgoing transactions (in terms of the addresses of resp. payer and recipient) are public, with date. Privacy is increased by using as many new bitcoin addresses as possible. There are mixing services that increase privacy. There is more privacy with the CryptoNote protocol, which is used by Monero, and has a kind of mixing service built into it. Privacy in relation to the government has the drawback of making it more difficult to detect tax evasion and other illegal practices. Cryptocurrency is considered to be a money laundering risk.
ICO
An initial coin offering (ICO) is a kind of crowdfunding in which a company or organization (whether or not with cryptocurrency as the main activity) sells digital tokens (a form of cryptocurrency) to the public. A majority of ICO’s use the Ethereum blockchain, partly because of Ethereum’s smart contract feature (ERC20 token standard). In many other cases, it uses its own blockchain.
Exchanges
A cryptocurrency exchange is a business that allows customers to trade cryptocurrencies or digital currencies for other assets, such as conventional fiat money or other digital currencies. A cryptocurrency exchange can be a market maker that typically takes the bid-ask spreads as a transaction commission for its service or, as a matching platform, simply charges fees.
According to a survey, In 2018 the top three cryptocurrency exchanges are Binance, Huobi, and OKEX.
Blockchain
The validity of each cryptocurrency’s coins is provided by a blockchain. A blockchain is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography. Each block typically contains a hash pointer as a link to a previous block, a timestamp and transaction data. By design, blockchains are inherently resistant to modification of the data. It is “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties in a verifiable and permanent way”. For use as a distributed ledger, a blockchain is typically managed by a peer-to-peer network collectively adhering to a protocol for validating new blocks. Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires collusion of the network majority. In the next free lesson I will shed some light on the technology behind cryptocurrencies: blockchain.
Or Enroll in the Pro Course & Become a Pro Trader!