The technology behind cryptocurrencies is called blockchain and is an unmistakably ingenious invention. As said in the previous lesson, it is invented by a person under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. But that might as well represent a group of people, nobody knows. Blockchain technology enables information to be distributed but not copied. In fact blockchain forms the basis of a new type of internet. The technology that came along with Bitcoin now finds other possible usecases.

Bitcoin is often considered to be the “digital gold”. But blockchains technology doesn’t have to be limited to the digital money usecase. Although you don’t really need to know how blockchain technology works in order to use it, I will shed some light on this topic in this free lesson. I will give you basic knowledge, so you will see why it is revolutionary. Lets start with some quotes about blockchain.
“Blockchain is a technological tour de force.”
– Bill Gates
1. Distributed Ledger
Blockchain is a digital ledger in which parties record transactions. Everyone remains the owner of their own coins or data. With smart contracts you indicate how others can use that data. The coins and data are encrypted and are only accessible with specific keys.

(Above: vintage ledger)
- Imagine a ledger that is copied many times across a network of computers.
- Now imagine that this network checks the original ledger regularly and updates the changes across the network.
This is in essence how a blockchain functions.
So the data that’s stored on a blockchain is like a shared database that is constantly checked. This technique has some obvious advantages. Most importantly, the database is not bound to a single location, which means that the contents are really public. This makes it easier to verify the data. It is more difficult to hack the data.
“Distributed ledger technologies offer institutions a once-in-a-generation opportunity to transform the industry to their benefit, or not.”
– PWC Report
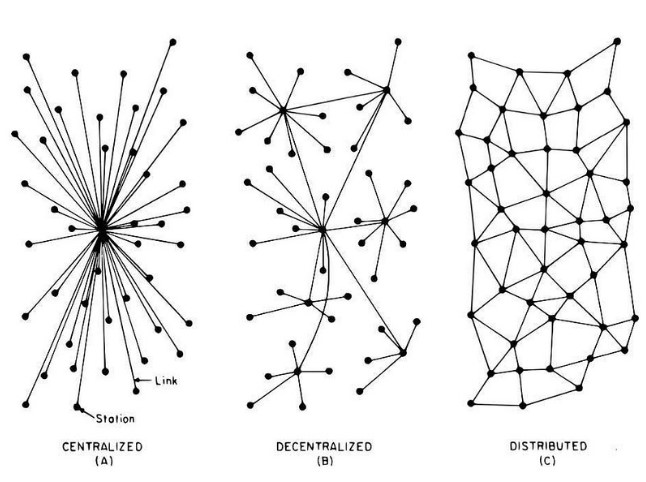
2. Decentralized
Blockchain technology has a inherent reliability. By copying identical information across its network, it doesn’t need a central controlling entity, and this is what makes it decentralized. Therefore it is less vulnerable. Everything that happens on the blockchain is a product of the network as a whole.
Since its invention in 2008 Bitcoin blockchain has operated without any significant problems related to the underlying blockchain technology.
This technology could have a number of important implications. By verifying transactions in this new way, traditional trade could change revolutionary. Every transaction would be executed in the blink of an eye on the blockchain, whether it be the stockmarket, or you local grocery. It could improve archiving like the cadastre.
But in the meantime it is already here. Just look at cryptocurrencies, and for example Bitcoin. Bitcoin is a blockchain network: a network of computers that collectively control the ledger with its transactions. Bitcoin has no central authority, but is controlled by the totallity of its peer-to-peer network.
Bitcoin is at the same time decentralized and also a distributed ledger network.
3. Consensus
Consensus is one of the most important aspects of blockchain technology. Consensus means the network continuously checks itself and reaches agreement on every transaction. Each batch of transactions is called a “block”. This results in two important properties:
• The network as a whole has to reach consensus, which gives it inherent transparency.
• Since it is not limited to 1 geographical location it is not possible to be hacked. To hack it, one would need an enormous amount of computing power, in order to hack the entire network. That would be a very expensive and unprofitable endeavour.
“Writing a description for this thing (bitcoin)
for general audiences is bloody hard. There’s nothing to relate it to.”– Satoshi Nakamoto
4. Nodes
The blockchain network consists of “nodes”. The nodes of the blockchain are the computers in the network. When joining the blockchain a node receives a copy of the current blockchain. The nodes validate and forward transactions. These nodes create a new kind of network, for example different from how the internet functions. Each node connects voluntarily to the blockchain, making the blockchain decentralized. The nodes mine the Bitcoins, it’s actually their incentive for participating in the network. Mining means nodes have to solve mathematical puzzles as soon as possible and get rewarded with Bitcoins. Blockchain was invented as part of the creation of Bitcoin. Nowadays there are many applications for the blockchain technology.

5. Keys
Storing data locally leads to particular risks. Storing it over a network eliminates these risks. Local data on a computer is vulnerable to hacking. Traditional computer systems use passwords for protection. Blockchain networks use encryption, based on “keys”. There are two kind of keys, public keys and private keys. A public key is like a bank account number. The private key is like your password to get access to it. Although data and value is safe on the blockchain, you can still lose your private key, or it can be stolen. This is why one should always print their private key. A printed key is also called a paper wallet.
The future of blockchain
Some call it the future, others call it a hype. A bunch of new technologies have been built and are being build around blockchain technology. Some of those will fail, and some of those will succeed.
Or Enroll in the Pro Course & Become a Pro Trader!